Initiatives for Natural Capital and Waste
- Basic Approach
- Effective use of water resources
- Proper management and reduction of waste
- Chemical substance management
Basic Approach
Based on our belief that biodiversity is essential for the global environment and the richness of our lives, the Olympus Group has taken action to conserve biodiversity through the management of water use and wastewater at each of its business sites and maintenance and management of green spaces as well as clean-up activities in the vicinity of business sites, forest conservation measures, and tree-planting. In recent years, it has been pointed out that the degradation of natural capital, including the land, oceans, freshwater, and air that contain biodiversity, could have major impact on the environment, society, and economic activities. Consequently, it is becoming increasingly important to identify risks and opportunities regarding which business activities depend on or have an impact on natural capital and to manage the key risks and opportunities in accordance with international initiatives such as the TNFD*1 and SBTs for Nature*2. Based on these developments, the Olympus Group began investigating using the LEAP approach, which comprises four steps: Locate, Evaluate, Assess, and Prepare. The LEAP approach is recommended by the TNFD as a means of appropriately evaluating and disclosing risks and opportunities relating to natural capital (land, oceans, freshwater, and air) in order to achieve a high degree of compatibility between conservation of natural capital and business activities. Below are the results of an early-stage investigation of the relationship between business activities and natural capital using the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) Biodiversity Risk Filter*3 and the results of an evaluation conducted using the World Resources Institute (WRI) Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas,*4 a water risk evaluation method that we’ve been using for some time.
*1 Task Force on Nature-related Financial Disclosures. An international organization that develops frameworks for appropriately assessing and disclosing risks and opportunities relating to natural capital and biodiversity in corporate activities. (Source: Ministry of the Environment)
*2 Science Based Targets for Nature. Measurable, actionable, and time-bound objectives relating to the interconnected systems of water, biodiversity, land, and oceans in value chains based on the best available science that allow actors to align with Earth’s limits and societal sustainability goals. (Source: Ministry of the Environment)
*3 Biodiversity Risk Filter. A regional biodiversity assessment tool based on information concerning biodiversity loss, including deforestation, pollution, and changes in land use for agriculture, created by the WWF.
*4 Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas. A water risk assessment tool created by the WRI.
Results of biodiversity and water risk assessment ![]()
Effective use of water resources
Water Use/Wastewater Results
| FY2024 Targets | FY2024 Results | Main Measures | FY2025 Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
Water use efficiency: improve compared to FY2023 |
Water use efficiency: improved by 2.8% compared to FY2023 |
|
Water use efficiency: improve compared to FY2023 (FY2026 water use efficiency: improve compared to FY2023) |
The Olympus Group uses water mainly in production processes, such as for cleaning components and cooling, as well as in its dining halls. We implement thorough wastewater control by adopting stricter standards than the legal requirements in each region, while setting targets for water use efficiency and furthering initiatives to reduce water consumption and wastewater emissions at those sites with high levels of water consumption. We are also acting to conserve water resources under collaborations with local communities at each site. Through these initiatives we have achieved a 2.8% improvement in water use efficiency in FY2024 compared to FY2023.
As part of major initiatives, at sites in Japan, Aizu Olympus has reduced water consumption by improving flow volumes for water used for cleaning in the manufacturing process, while Aomori Olympus has also reduced utilities water consumption by switching to water-saving toilets. In Europe, Olympus Medical Products Portugal, Unipessoal LDA introduced a water treatment system for industrial wastewater, and reuses all treated water to water gardens, thereby endeavoring to effectively use water resources.
For cooperation with local communities, Olympus Surgical Technologies America (formerly Gyrus ACMI, Inc.) in the U.S. received a Silver Award* in recognition of efforts to maintain compliance with the industrial wastewater discharge permit requirements set by King County, Washington.
In addition, we are raising awareness of the importance of conserving water resources and of water-saving initiatives via awareness-raising programs for all employees.
In FY2025, with the objective of again improving our water use efficiency compared to FY2023, we will promote water-saving initiatives through improvements to facilities and manufacturing processes as well as the secondary use of water.
* Presented to companies that have met the standard of the Silver Award set in the program of industrial wastewater discharge permit requirements by King County, Washington.
Commitment-to-Compliance Award ![]()
Water Use
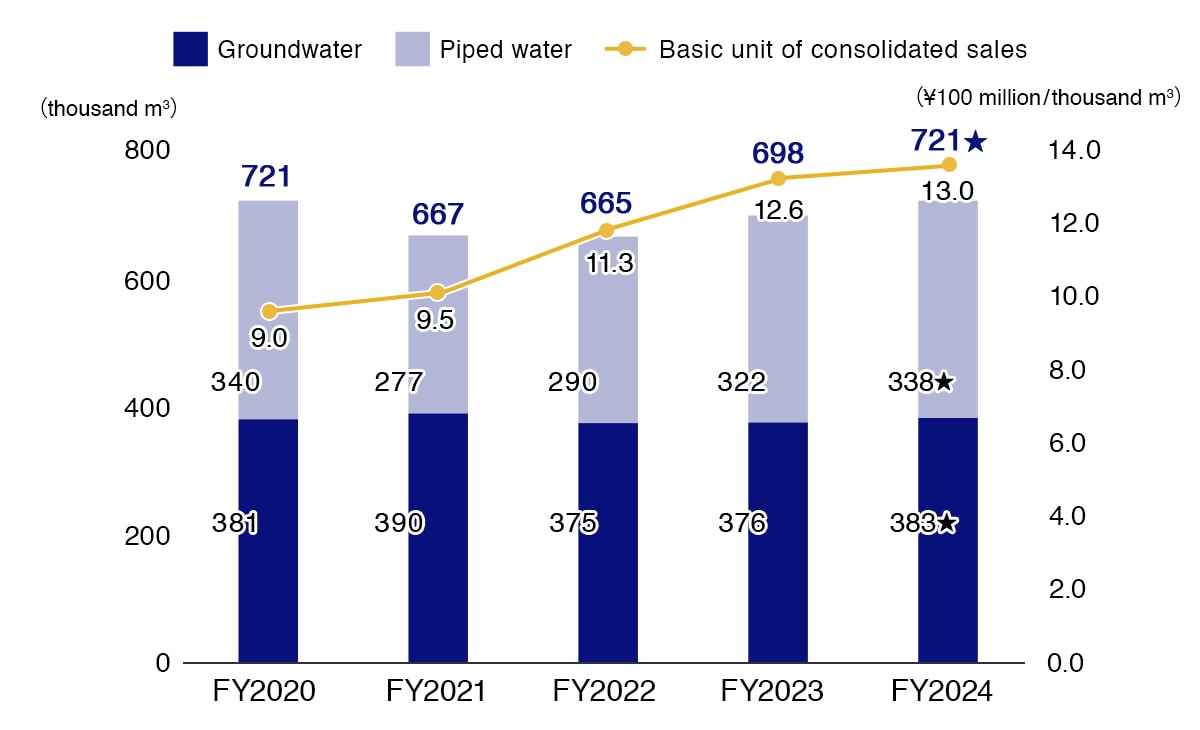
★ Indexes certified by external assurance.
Water Use
Wastewater Results
Proper management and reduction of waste
Waste Emissions Results
| FY2024 Targets | FY2024 Results | Main Measures | FY2025 Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
Waste recycling rate: at least 85% |
Waste recycling rate: 84% |
|
Waste recycling rate: at least 86% (FY2026 waste recycling rate: at least 87%) |
The Olympus Group is working continually on reducing losses in manufacturing processes by making improvements to them and efficient use of resources, including thorough waste separation to reduce waste discharge, extract valuable materials and promote recycling. In FY2024, the waste recycling rate was unchanged from the previous year, at 84%.
As part of major initiatives, at sites in Japan, we promoted the conversion of scrap metal from fixed assets into valuable materials at the Hinode Plant and the recycling of work clothes at Aizu Olympus.
In the Americas, Olympus Surgical Technologies America Inc. is promoting the recycling of PPE waste (personal protective equipment used at medical facilities, etc.) at its Bartlett site. In addition, the Bartlett site signed up to the “Tennessee Recycling Coalition”* to explore new ways of recycling, develop and expand the reuse and recycling market, and continue to study ways to further reduce waste. The San Jose site promoted the reuse of package cushioning materials and the Redmond site promoted the conversion of waste into compost. Olympus Vietnam Co., Ltd. (OVNC) optimized its waste disposal by means of undertaking a consideration of appropriate waste processing and disposal contractors and a review of waste disposal methods.
In response to hazardous waste, we are promoting substitution with low hazard materials and recycling, and although the volume of activities increased significantly in FY2024, emissions levels remained largely unchanged from FY2023.
The Olympus Group outsources the appropriate processing and disposal of those wastes generated that are difficult to reuse in-house to specialized waste processing and disposal contractors.
In Japan, we implement on-site inspections of industrial waste processing and disposal contractors to coincide with the conclusion of new contracts or once every three years, to safeguard against illegal or improper disposal by waste processing and disposal contractors, and thereby confirm that appropriate outsourced waste processing and disposal is being carried out.
We will continue to seek out novel recycling methods and actively promote further measures to reduce the amounts of waste generated toward achieving a waste recycling rate of 86% or more in FY2025.
* Tennessee Recycling Coalition: A non-profit organization dedicated to promoting recycling and sustainable materials management practices in Tennessee, U.S.
Waste Emission/Landfill
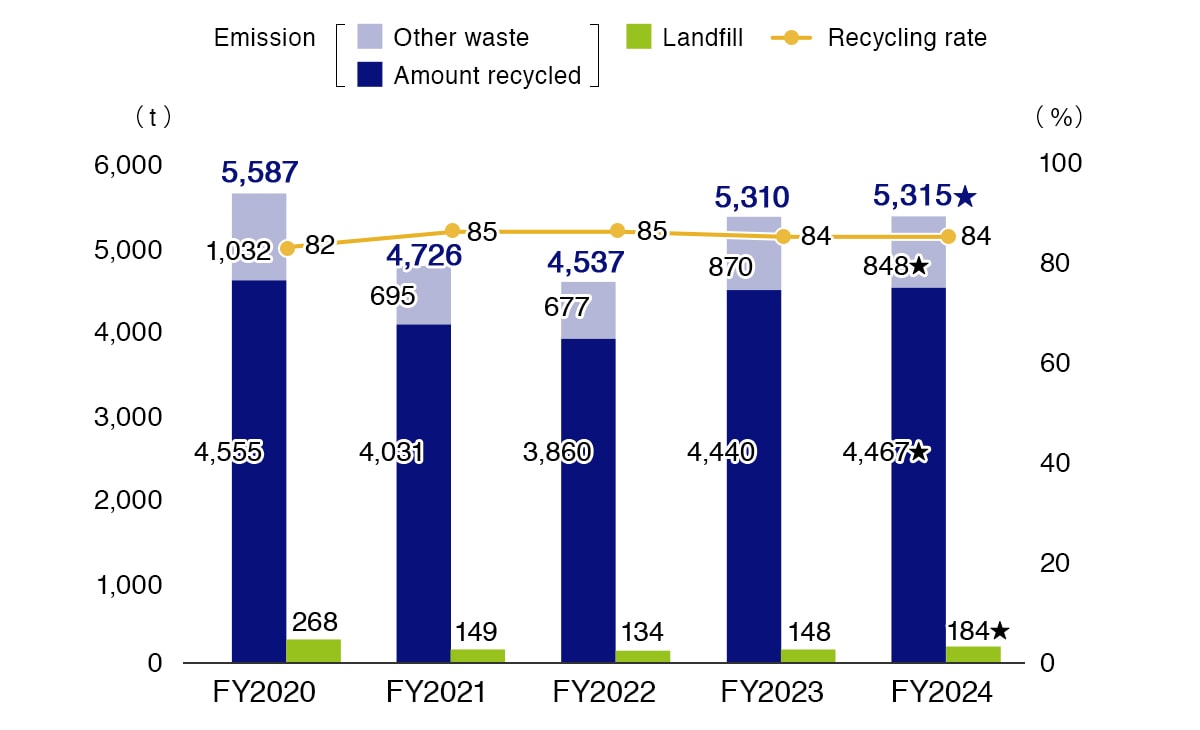
★ Indexes certified by external assurance.
Waste Emission/Landfill
Hazardous Waste Discharged
Recycling of PPE waste (personal protective equipment at medical sites, etc.)

Promoting waste separation and composting

Chemical substance management
Chemical Substance Safety and Control
| FY2023 Results | Main Measures |
|---|---|
Emissions and Movements of PRTR Class 1-Designated Chemical Substances: Reduced by 1% |
|
The Olympus Group is striving for appropriate management and emissions reduction of chemical substances subject to the PRTR regulations and volatile organic compounds (VOC) in order to minimize the impact on people and the environment. In workplaces at which chemical substances are used, we are substituting with safer chemicals and implementing risk reduction measures through environmental impact assessments and chemical risk assessments prior to the introduction of new chemical substances.
Emissions and Movements of PRTR Class 1-Designated Chemical Substances
| FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emissions and Movements of PRTR Class 1-Designated Chemical Substances | 17 | 13 | 12 | 10 | 10 |
* Scope: Manufacturing and development sites in Japan
Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Emissions
| FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volatile Organic Compound (V OC) Emissions (t) | 67 | 39 | 41 | 45 | 47 |
* Scope: Manufacturing and development sites in Japan

