Worldwide trends in esophageal cancer
1. Sex disparities
Approximately 70% of all esophageal cancers in the world occur in men, making it more common in men than in women.
2. What are the risk factors?
The risk factors for esophageal cancer include obesity, alcohol consumption, smoking, consumption of hot beverages, and diseases like gastroesophageal reflux disease, Barrett's esophagus or damage to esophagus, and rare conditions like esophageal achalasia. Eating vegetables and increasing physical activity is known to decrease the risk.

The incidence of esophageal cancer is closely related to age; more than 85% of the patients in the United States are over 55 years of age. The risk of getting esophageal cancer increases with age.
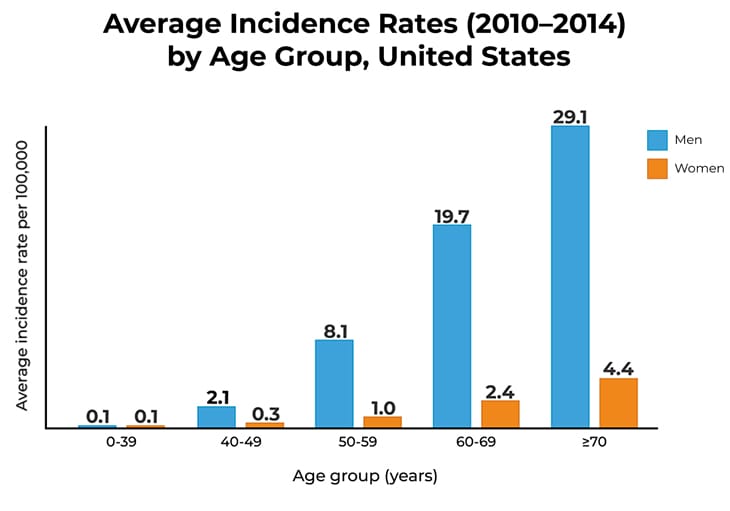
Source:
Islami F et al. Incidence Trends of Esophageal and Gastric Cancer Subtypes by Race, Ethnicity, and Age in the United States, 1997–2014. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17(3): 429–39.
3. Early detection is key to survival
The 5-year survival of esophageal cancer has increased in the United States from 5% in the 1970s to approximately 20% now, a number which includes early detection cases as well as advanced cancers. Esophageal cancer is often diagnosed after it has progressed, but early detection can greatly increase survival. Therefore, early detection of esophageal cancer is crucial.
This column has been prepared under the supervision of a physician for the purpose of providing general information on cancer.
It is not a substitute for the advice and services that should be provided by a physician or other healthcare professional. If you notice any health conditions, please consult your family doctor or a specialist.

