Let's Learn about Endoscopes
1. What Is the Role of a Medical Endoscope?
Food which comes in through the mouth is digested in the stomach, and nutrition is absorbed in the small intestine, etc. and moisture is absorbed in the large intestine, before it is discharged through the anus.
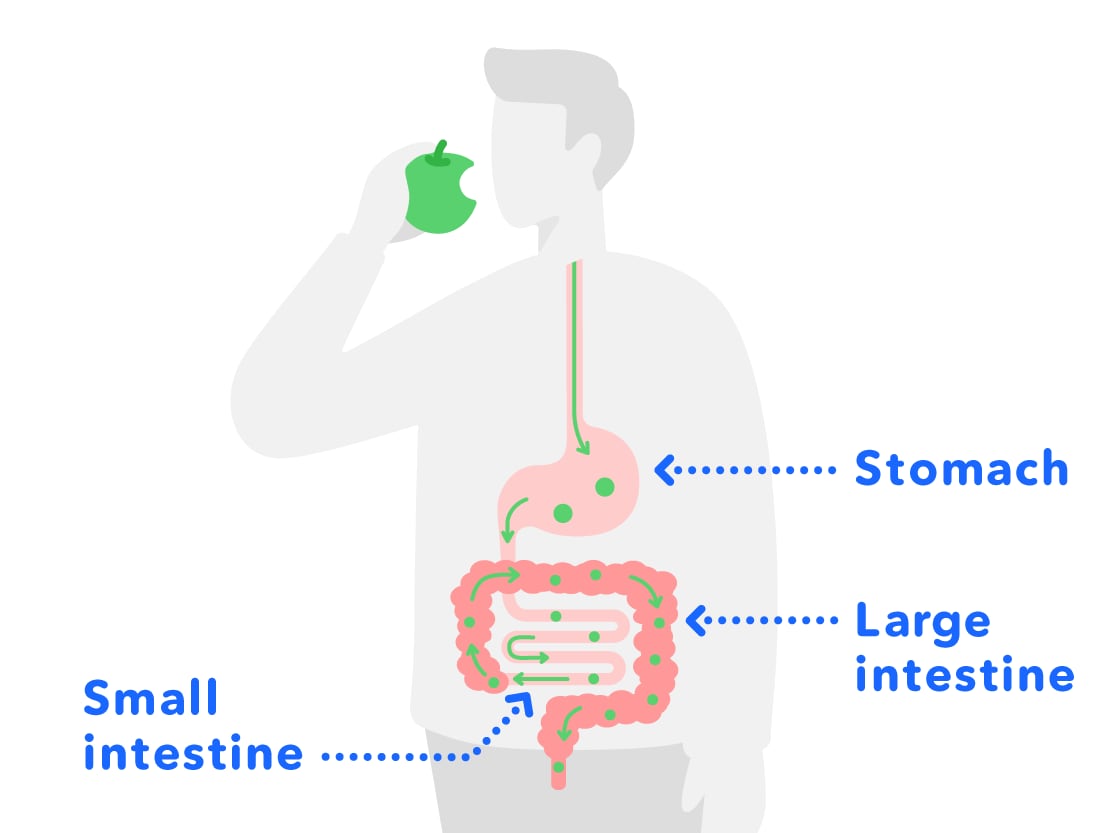
If your stomach or large intestine was to get sick, you can't see them from the outside, so how do you think we can see the sick parts and remove them?
Of course, doctors can't directly see your abdomen or put their hands inside your abdomen through your mouth to remove the sick parts!
The medical tool that doctors use to look inside of your abdomen without opening it up (examination) and to remove the sick parts (treatment) is called a medical endoscope. Endoscopes are medical tools which can be used as the "eyes" and "hands" of doctors.
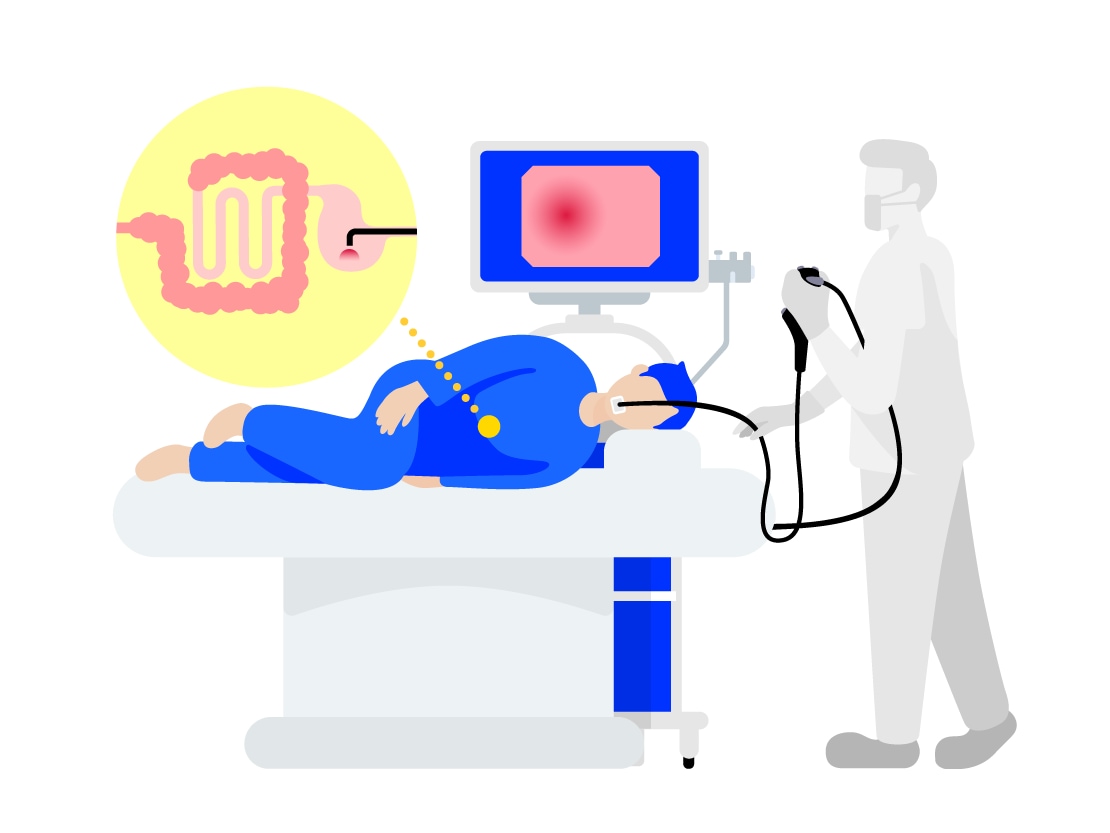
2. Types of Endoscopes
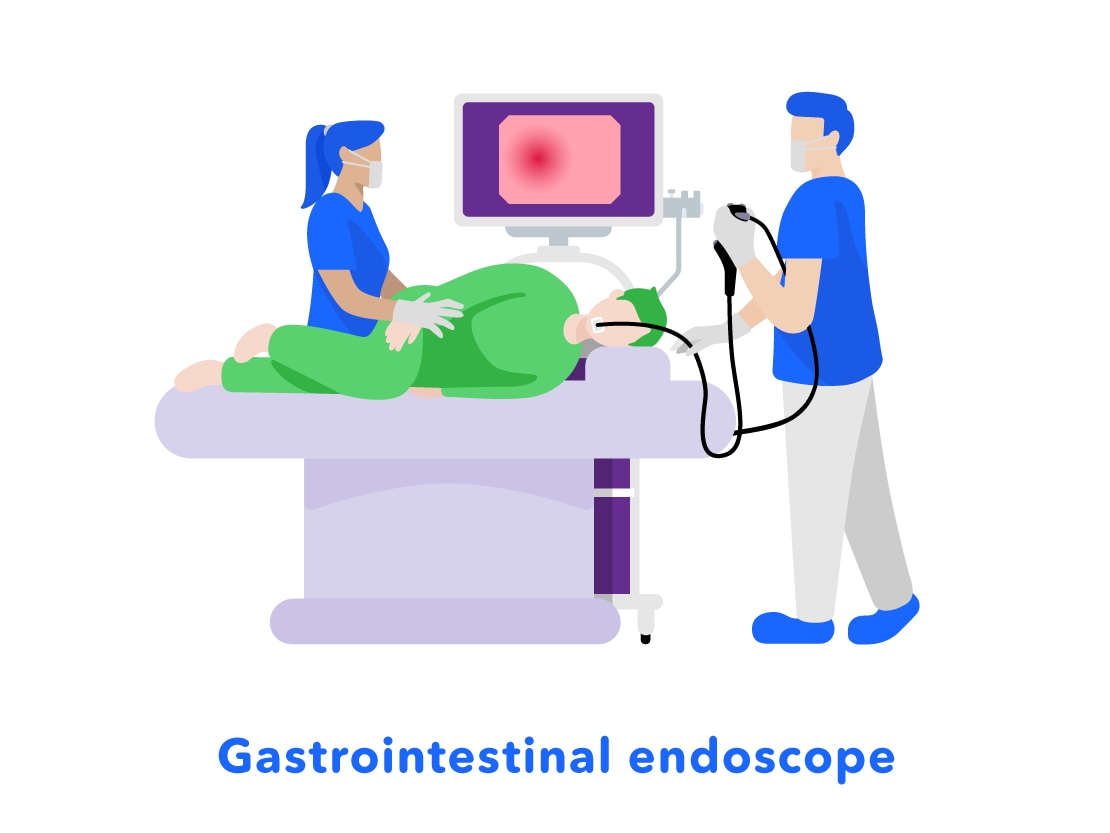
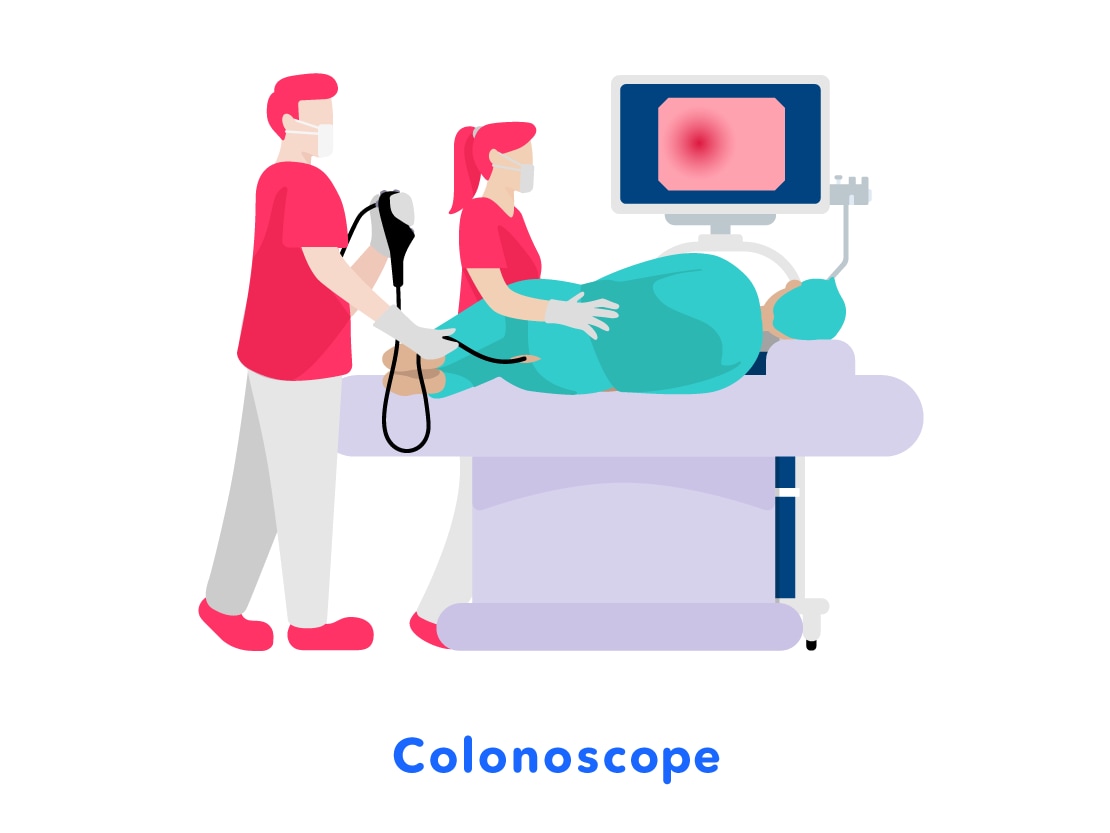
There are different types of medical endoscopes. For example, there are "gastrointestinal endoscopes" used to examine and treat the stomach through the mouth or nose, and "colonoscopes" which are used to examine and treat the colon through the anus.
3. Importance of Early Detection and Treatment of Cancer
So, let's talk a little about this disease called "cancer". Cancer is a scary disease which, if left alone, can spread to other parts of the body and can cause people to die. Cancer is believed to have a strong connection to life habits such as smoking, eating habits and exercise. It is believed that lifestyle improvements such as stopping smoking, modifying eating habits, and improving poor exercise habits are all effective at preventing cancer. However these alone cannot completely prevent cancer.
Also, early detection and early treatment of stomach cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer and cervical cancer are known to reduce the mortality rate. Along with a lifestyle which is good for the body, "early detection and treatment" through examinations is very important. Endoscopes, which are able to see inside of the body, help doctors with the early detection and treatment of stomach and colon cancers.
Differences in 5-year Survival Rates by Disease Stage
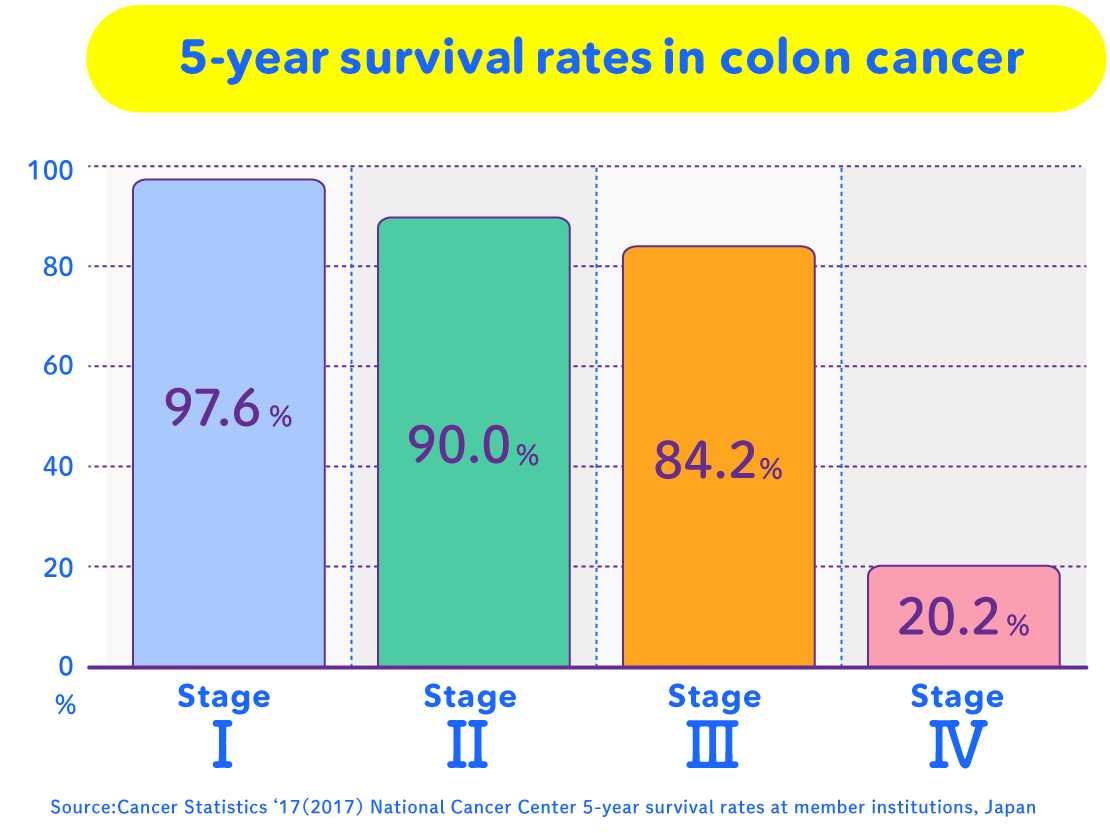
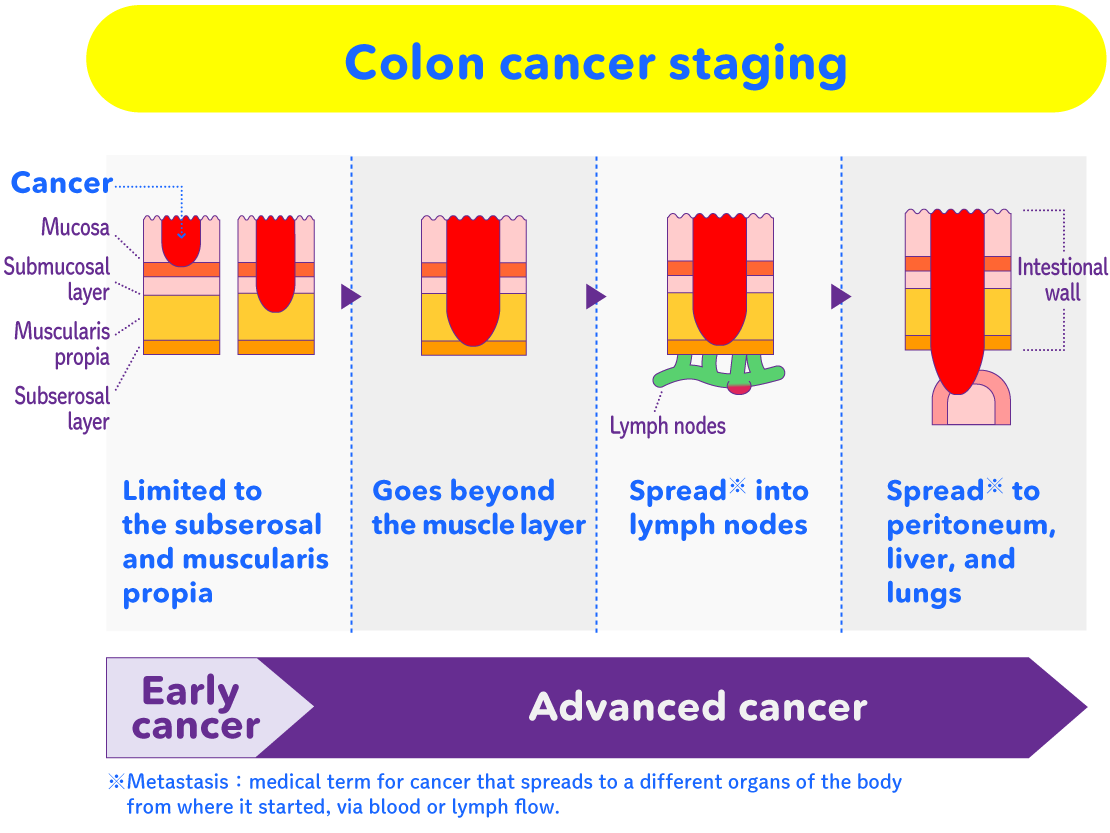
These endoscopes, which help so much in "early detection and treatment of cancer", have gone through a lot of innovations to get to their present form.
We will now look at the history of the development of the endoscope.
4. History of Endoscope Development
- Efforts to See the Internal Organs of People -
In 1868, a German doctor was the first to see the inside of a stomach by having a sword-swallower swallow a straight metal pipe called a gastroscope. It also came to Japan, but didn't spread very well because swallowing it was painful for patients.

5. World's First Practical Application of the Olympus "Gastrocamera"
In 1949, Olympus, who produced cameras, was asked by a doctor in Japan if they could "create a small camera which could see inside of the stomach without cutting it open". Around this time many people in Japan were dying from "stomach cancer", so there was a desire to quickly find and treat stomach cancer.

Olympus conducted repeated research and experiments, making the parts to be placed inside of the body smaller and softer.
Then, in 1950, the world's first "gastrocamera" prototype was developed, which was able to take photos of the inside of the stomach for the first time.
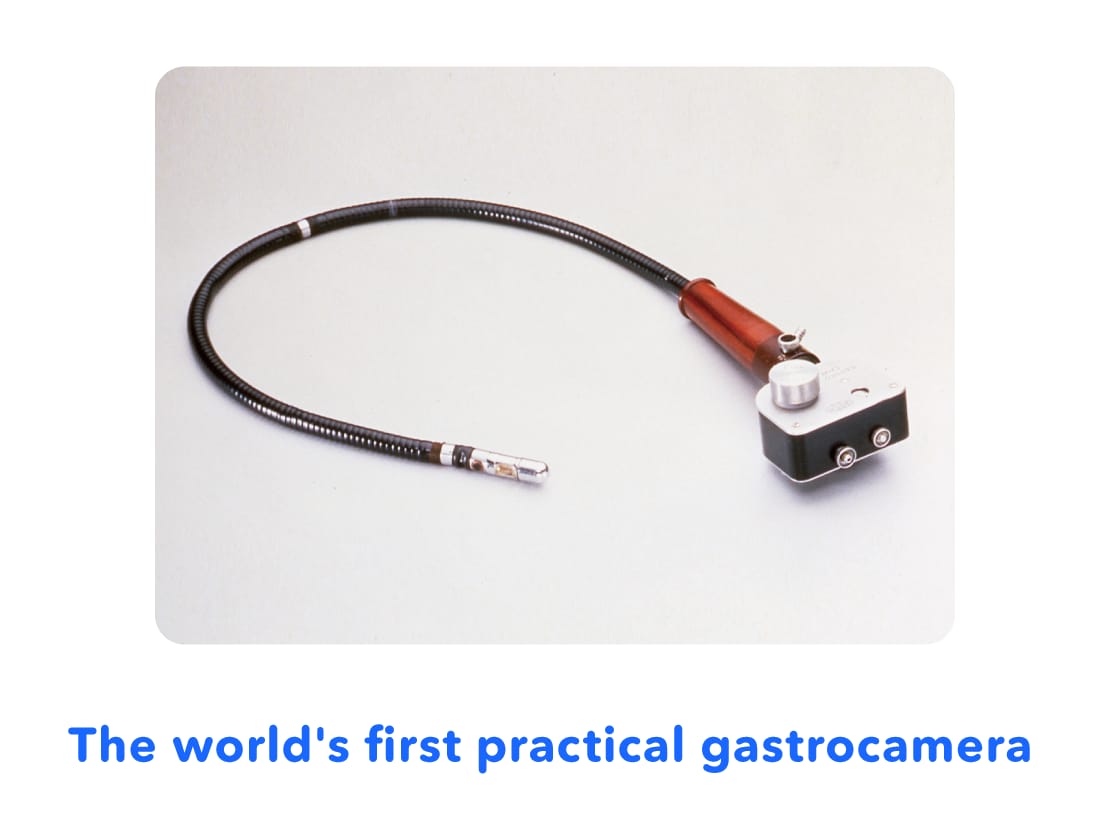
The gastrocamera had a camera lens and flash on the tip that was swallowed. The inside of the stomach could be filmed by pressing the shutter button on the device outside of the stomach. Images were recorded on film, which was developed after the examination*, allowing the inside of the stomach to be checked.
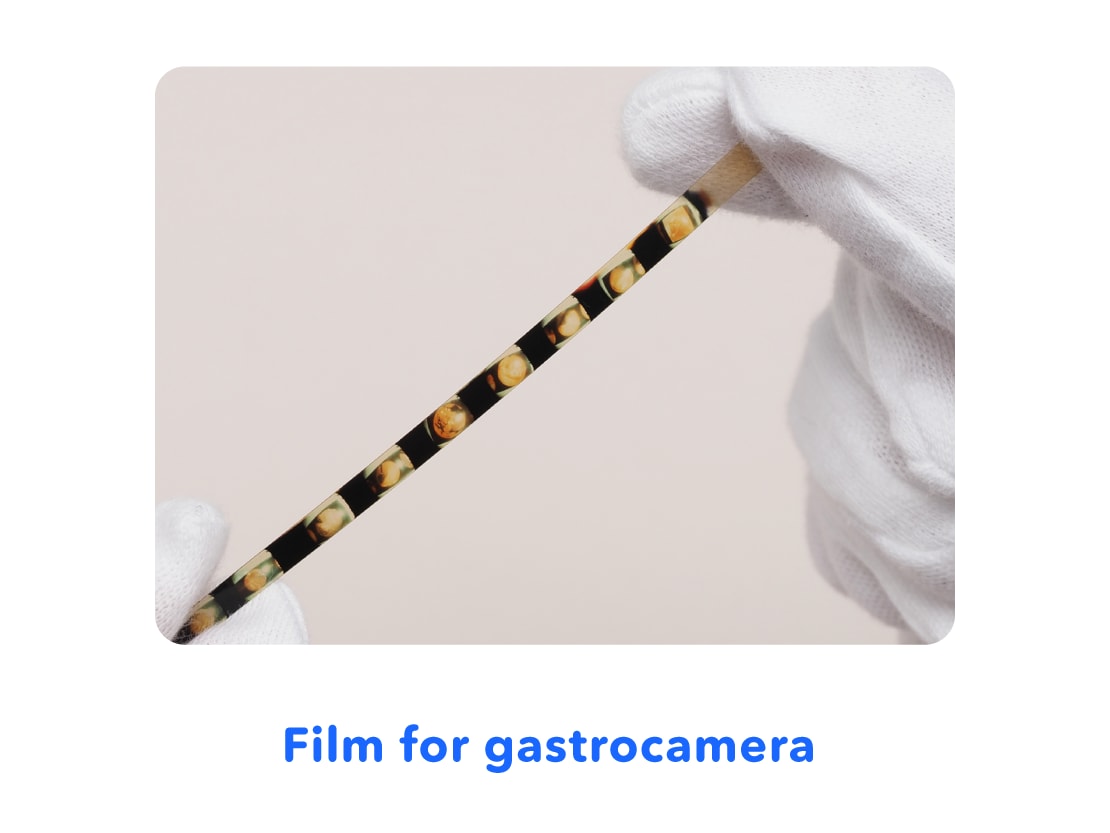
* What is Developing: Film on which images have been shot and recorded is immersed in chemicals to show the image that was shot. After drying, a photograph is produced.
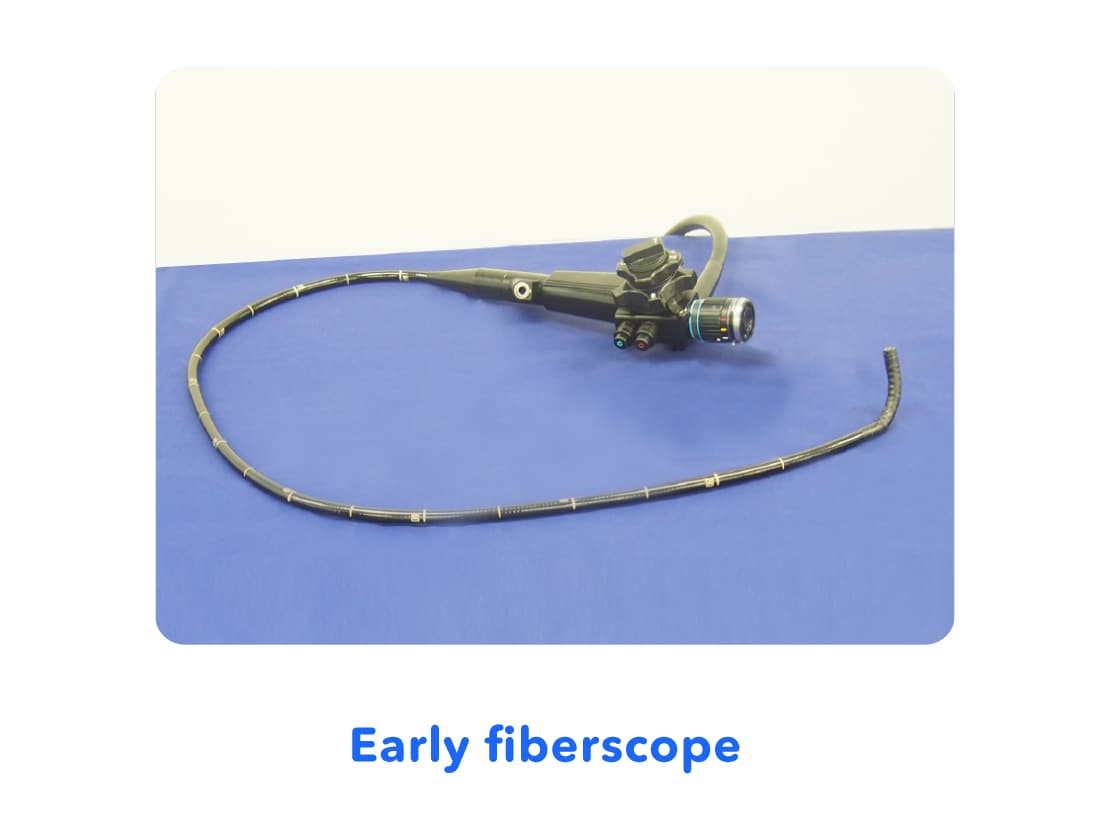
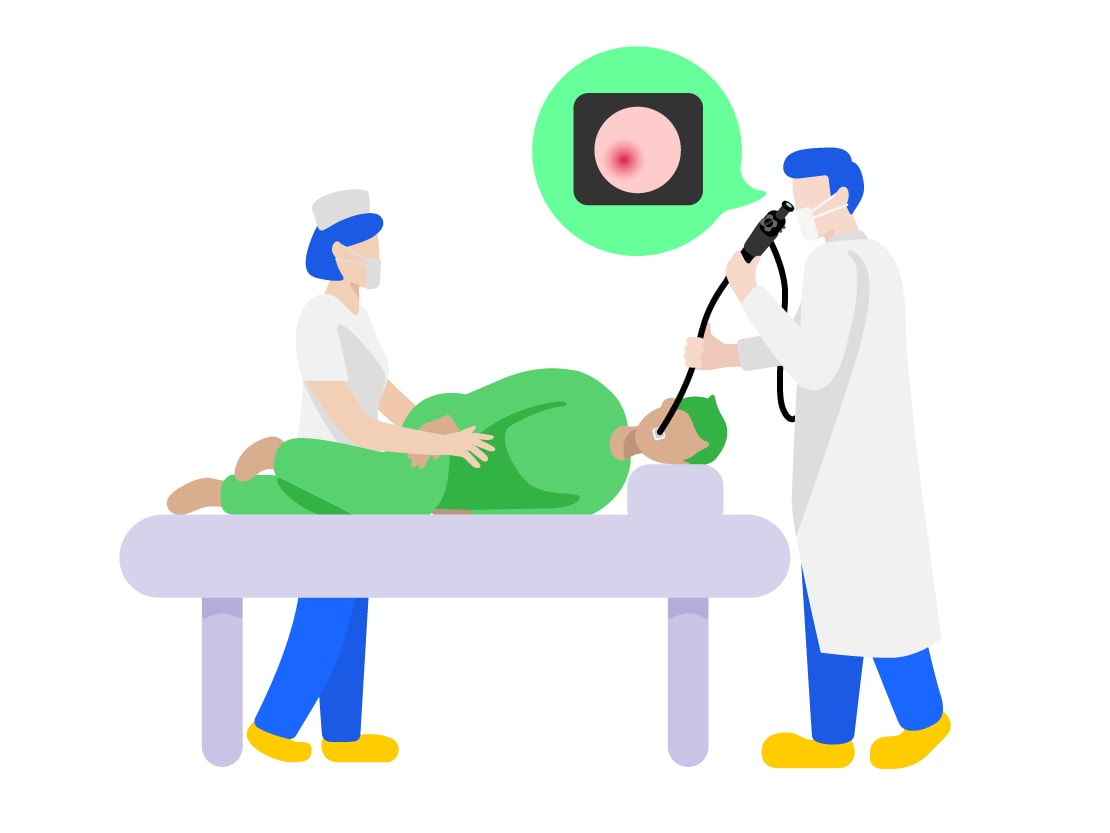
6. Spread of "Fiberscopes"
In the 1960s, the "fiberscope" emerged, which used a material known as glass fiber. Glass fiber played the role of a long lens which could be bent and convey light from one end to the other end. By using a bundle of these glass fibers, the fiberscope allowed the inside of the stomach captured at the tip of the scope* to be seen at the other end. This "fiberscope" made it possible for doctors to see inside of stomachs immediately, during their examination.
* What are Scopes: Long shaped medical devices which can have the tip placed inside of your abdomen so that the inside can be seen at the other end.

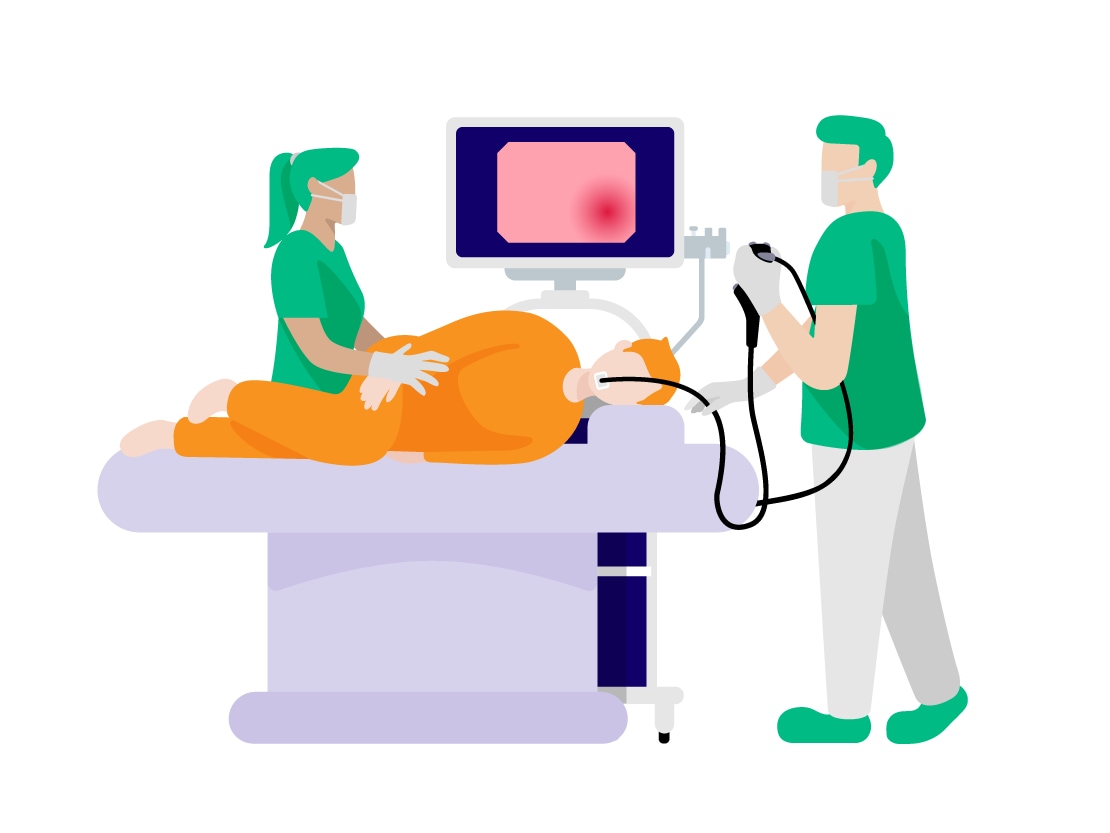
7. Spread of "Videoscopes"
In the 1980s, "videoscopes" emerged, with video cameras with ultra-small parts called charge-coupled devices (CCD) incorporated into scopes. This videoscope is the system used today for endoscopes.
Videoscopes allow the video images of the inside of the abdomen captured by the video camera at its tip to be displayed on a monitor. This made it possible for multiple doctors and nurses to see the inside of the abdomen, instead of just one doctor previously, contributing more accurate diagnosis and treatment of diseases.

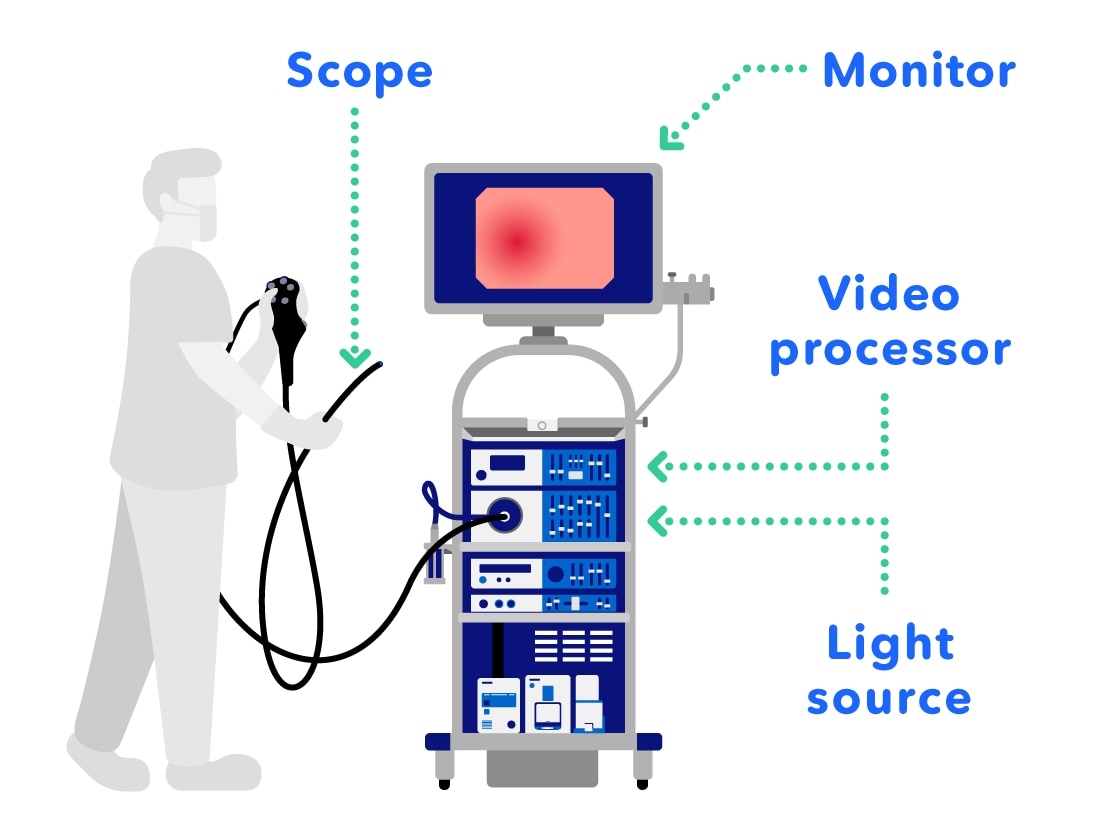
8. Configuration of Endoscope Systems
Endoscopes are a combination of different devices. Firstly, the system consists of a video processor which processes the images taken with the tip of the scope inside of the abdomen and displays them on a monitor.
Because the inside of the abdomen is dark, a light source is used to emit light from the tip of the scope, making the inside of the abdomen bright.
System Introduction
There is also a "treatment tool" which is used together with the endoscope to remove diseased parts.
Inside of the scope is a tunnel-like part called the "instrument channel" which is used for the treatment tool to pass through. There are many different kinds of treatment tools, depending on the application.
Scope Introduction
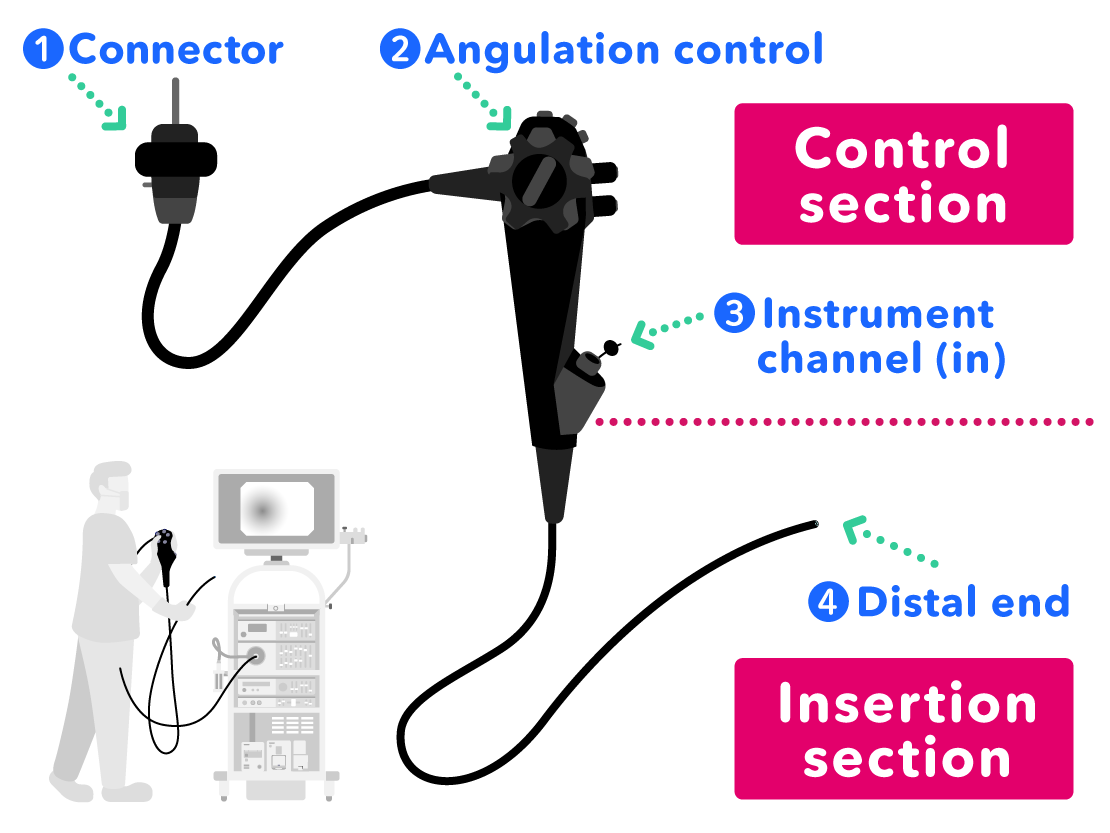
- Connector: to connect the scope to the light source
- Angulation Control: to control the direction of the scope tip by hand
- Instrument Channel (In): to insert treatment tools into the instrument channel in the scope
- Distal End: placed into the abdomen to check the state inside
Introduction to the Distal End of the Scope
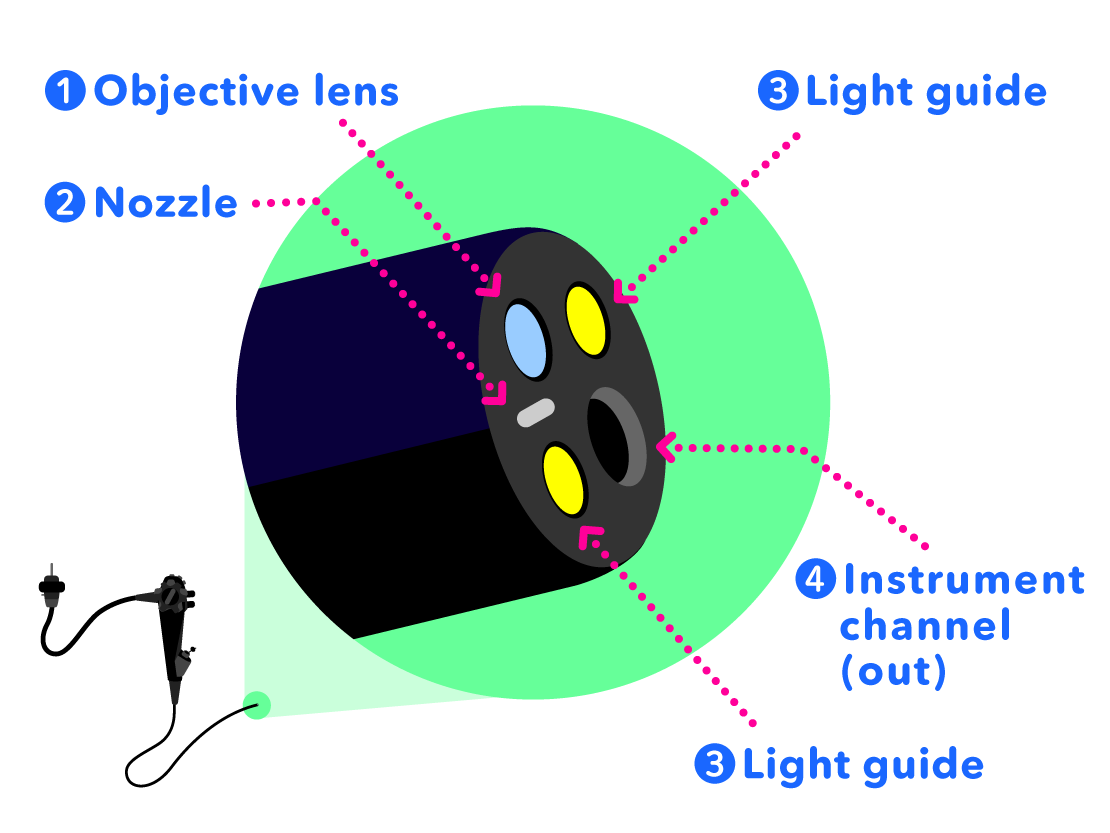
- Objective Lens: to see the inside of the abdomen
- Air/Water Nozzle: to inject air so as to inflate the abdomen to make it easier to see inside, or to inject water to clean the objective lens surface
- Light Guide: to light up the dark insides of the abdomen
- Instrument Channel (Out): treatment tools come out through the instrument channel
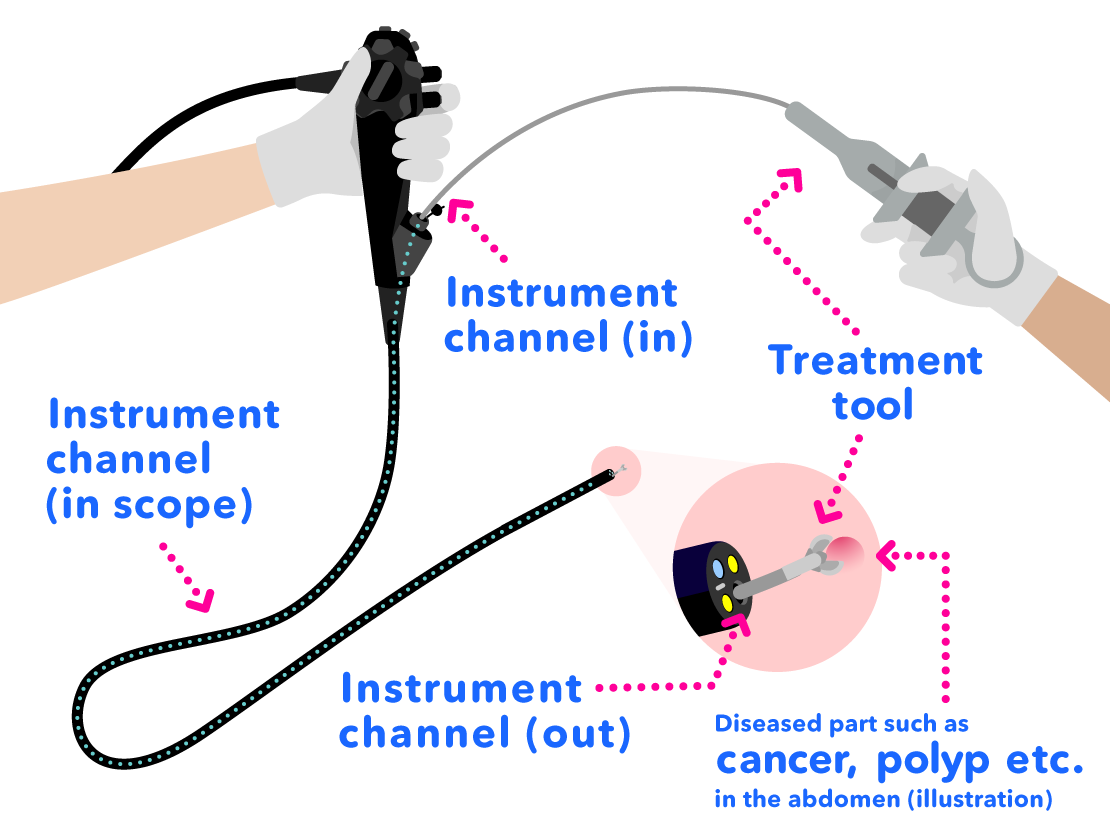
Treatment Tool and Instrument Channel
Treatment tools which are placed into the instrument channel (in) at the grip of the scope pass through the instrument channel and come out of the instrument channel (out) at the distal end of the scope.
Various Types of Treatment Tools
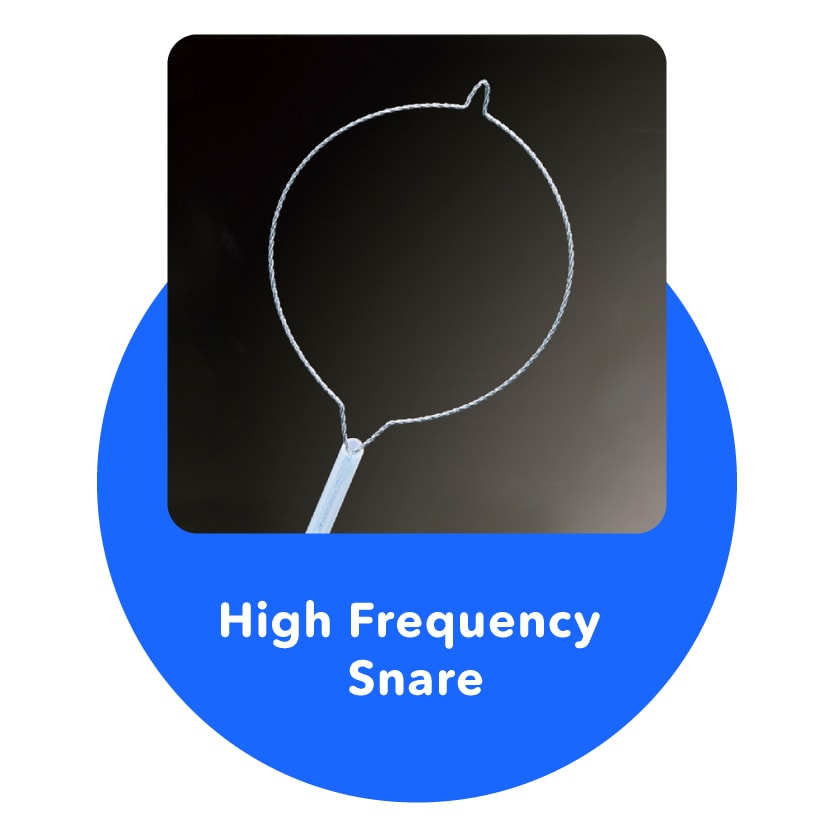
High Frequency Snare
Treats diseased parts in the stomach or colon by placing a round snare around them and removing them by squeezing.

Biopsy Forceps
Used to pinch and remove parts that are or may be diseased from the stomach or colon.
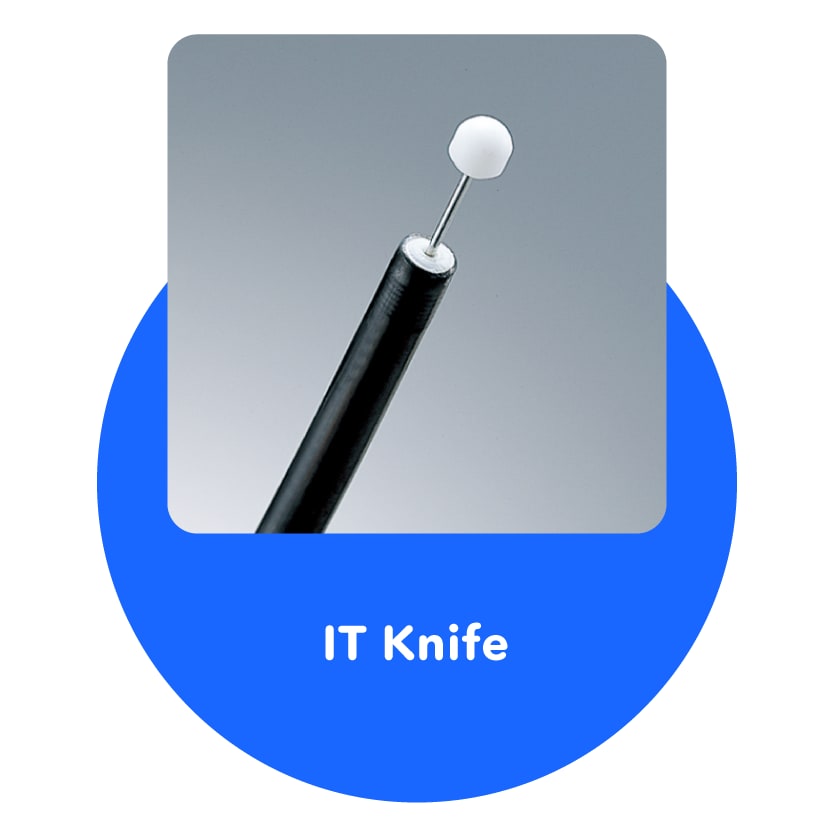

IT Knife
Cuts and treats diseased parts in the stomach or colon.
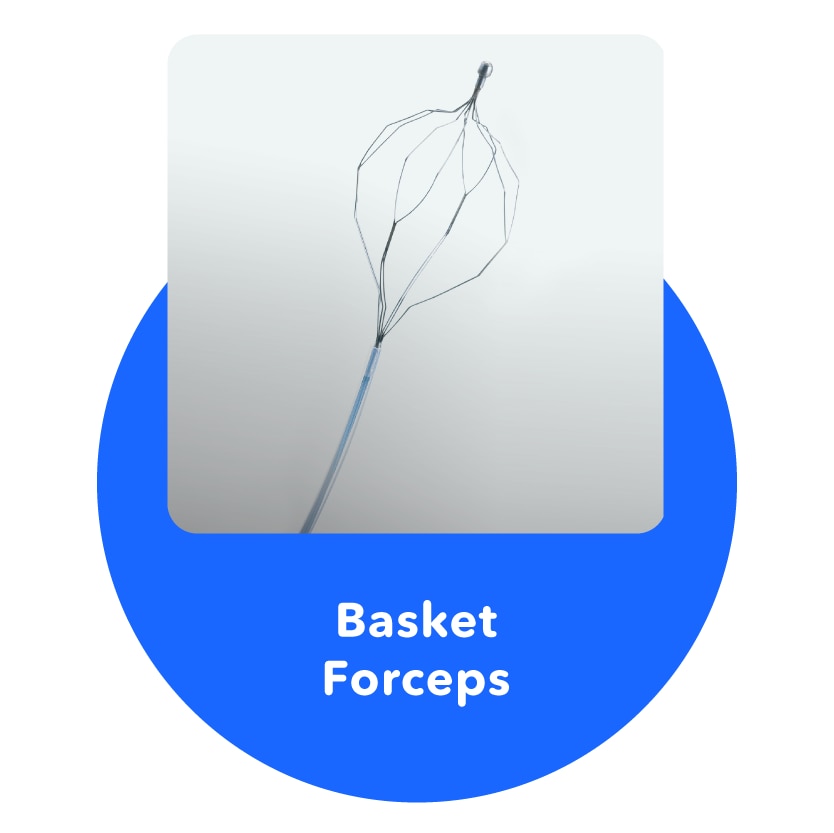

Basket Forceps
A treatment tool for removing foreign objects from the stomach or colon.

Needle
Able to inject directly into diseased parts.
9. New Technology Narrow Band Imaging (NBI)
Next, we will introduce the latest Olympus technology, Narrow Band Imaging (NBI), which uses special light properties. When you see sunlight, it looks like it is colorless and transparent "white light". But actually, light is a mixture a three primary colors "red, green and blue", which look transparent when they are mixed together.
When colorless and transparent light (white light) is acted upon in some way and refracted, it separates into several colors. You can see several different colors when you see a "rainbow", which is created when the sun's light is refracted by water drops in the sky after it rains.
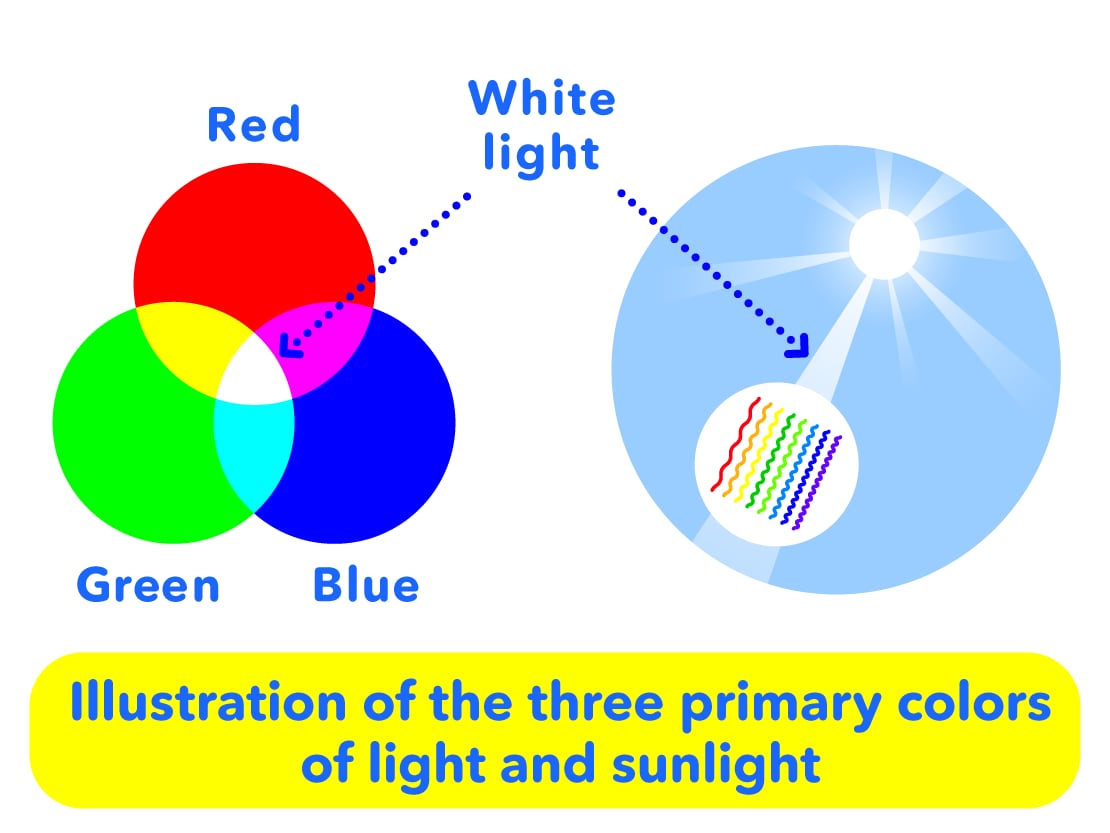
Endoscopes also normally show "red, green and blue" light processed into a monitor, but this new narrow band imaging (NBI) is the latest technology which uses only light with the specific wavelengths of "blue and green."
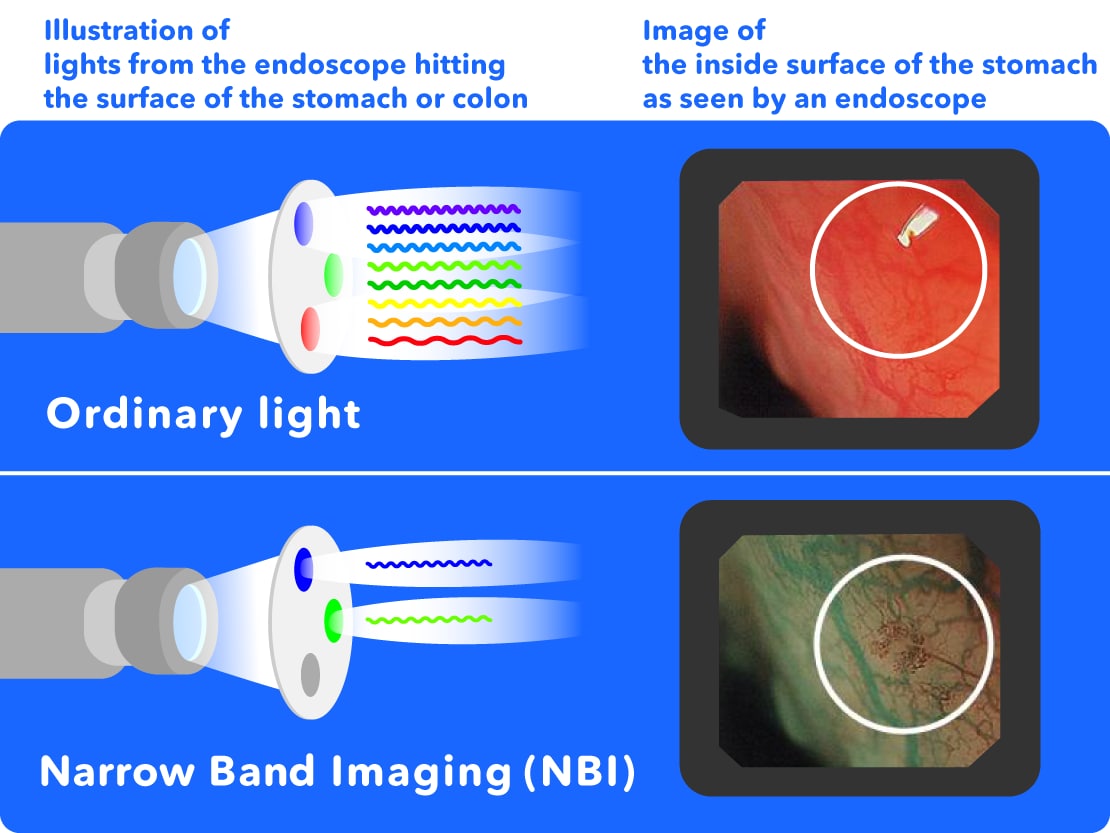
When the specific light of the NBI hits the surface of the stomach or colon, it can easily show groups of capillaries which can be difficult to see with normal light. Because cancer obtains its nutrients through blood vessels, blood vessels are thought to collect around cancers. NBI makes it easier to see these collections of blood vessels, supporting doctor's examinations and allowing for the early detection of cancer etc.
In this way, endoscopes continue to evolve every day. Olympus will continue to work hard on research and development to assist doctor's in the early detection and treatment of diseases, for the maintenance of everybody's good health.

