Endoscope Repair Service
The high quality of endoscope repair builds trust in medical practices around the globe.
A high-quality system exists for repairing and maintaining the endoscopes used in the unforgiving environments of medical practices around the world, and this system continues to provide healthcare professionals with safety and security.
Departments in the head office and Olympus' overseas affiliates work together to provide the highest level of quality in a system constructed based on friendly competition. Now when healthcare professionals visit one of these endoscope repair centers, they are always impressed by the meticulous and ingenious repair and quality assurance systems.
Where to Begin?
Olympus has established an industry-leading global service network with over 200 repair centers worldwide, so that the world’s patients could receive endoscopic examinations and treatments with peace of mind. The scope of this network leads to stronger contact points with customers, and supports Olympus' endoscope business. At the same time, the importance and difficulty of maintaining repair quality has also been indicated.
In 2004, Olympus began a program of activities aimed at improving the quality of repair centers around the world. At first, none of the persons involved were sure where to begin with the many repair centers, as they attempted to find a way to move forward. From a recognition that repair work is a part of the manufacturing process, the focus was first placed on quality control in manufacturing, and the improvement activities started by taking a hint from the quality auditing used to evaluate manufacturing plants.
Global Repair Service Network
PDCA Applied by Sharing Issues with Overseas Affiliates
First, a quality assurance system audit was conducted based on factory standards at the repair centers of Asian affiliates, in order to clarify basic improvement tasks. Staff at both the Tokyo head office and local offices then took this opportunity to come together as a team and implement improvements at a fever pitch.
Discussions were held regarding these shared tasks until both sides were convinced of the plan of action, employees at the workplaces were brought onboard, and a program of reform in quality awareness was implemented. This approach of coming together to achieve solutions was one of the factors behind the effort successfully continuing for such a long period of time, as it inspired the involvement of the affiliates.
Requirements Created for Providing Olympus Service
Next, it was determined that it would be necessary to expand these activities to Europe as well. At the time, in 2004, the head office of the European affiliate was conducting independent quality audits (reviews) based on ISO 9001, and so there was resistance to the idea of the Tokyo head office conducting quality audits.
At this point, the key managers of European repair centers were brought together at Aizu Olympus and Shirakawa Olympus in order to introduce them to the quality control systems employed by the factories in Japan, as well as aspects such as the production improvement efforts being carried out as well as the 5S activities. The European managers learned about the hard work focused on improvement at the factory workplaces, and then incorporated these improvement activities at the repair centers as well. In order to make it easier to apply the system to the European repair centers, it was proposed that the previous "Quality Audit" method would be revised into a "Quality Review" method, and implementation began in Europe.
Furthermore, as a common global policy for repair services, shared indices were created that anyone could agree with, and the same set of “Global Technical Service Guidelines” was established for the entire Olympus Group with the goal of ensuring that the same quality would be provided worldwide. This "Quality Review" method was adopted worldwide, and it helped build stronger relationships with overseas affiliates around the globe.
Spiraling Upward with Friendly Competition
Current capabilities are evaluated using a point system based on shared global guidelines, and the results of improvements are then evaluated once again. The evaluation points received during these Quality Reviews can also be seen by other overseas subsidiaries. In addition, excellent efforts are honored, and a mechanism was created whereby such efforts can be introduced to other overseas affiliates.
At first, some hesitated at the prospect of disclosing these report cards to the entire world. However, this allows affiliates to see their own levels of effort and positioning, and the system works as a benchmark that spurs friendly competition, dramatically accelerating the "spiraling up" process of improved quality.
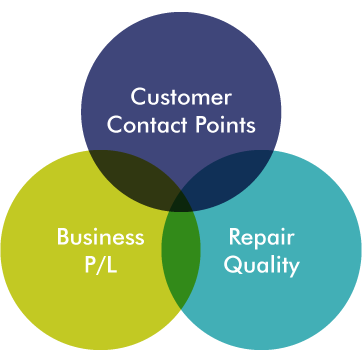
The three service components of the "Global Technical Service Guidelines": Balance between these three components is the basic philosophy behind Olympus' service.

"Global Technical Service Guidelines": Of the three components of repair quality, customer contact points, and business P/L (profitability), the main focus is on repair quality.
A Licensing System to Maintain Quality
As a result of these efforts, the rate of returns was cut in half, and deadlines were complied with. Also, in concert with these improvements in quality, customers were shown around the repair centers in tours as part of an activity referred to as "Showcase Service".
This was a marketing activity designed to gain trust by showing the customers the actual repair sites. It was through these steady efforts that customers began to flock to Olympus for the high level of repair quality.
During the next stage of repair service quality improvement, efforts aimed at improving overall organizational quality shifted towards an approach designed to improve quality and skill levels at the individual level. At present, progress is being made in introducing a licensing system for all global repair and service professionals.
Repair Center Improvements through Quality Reviews
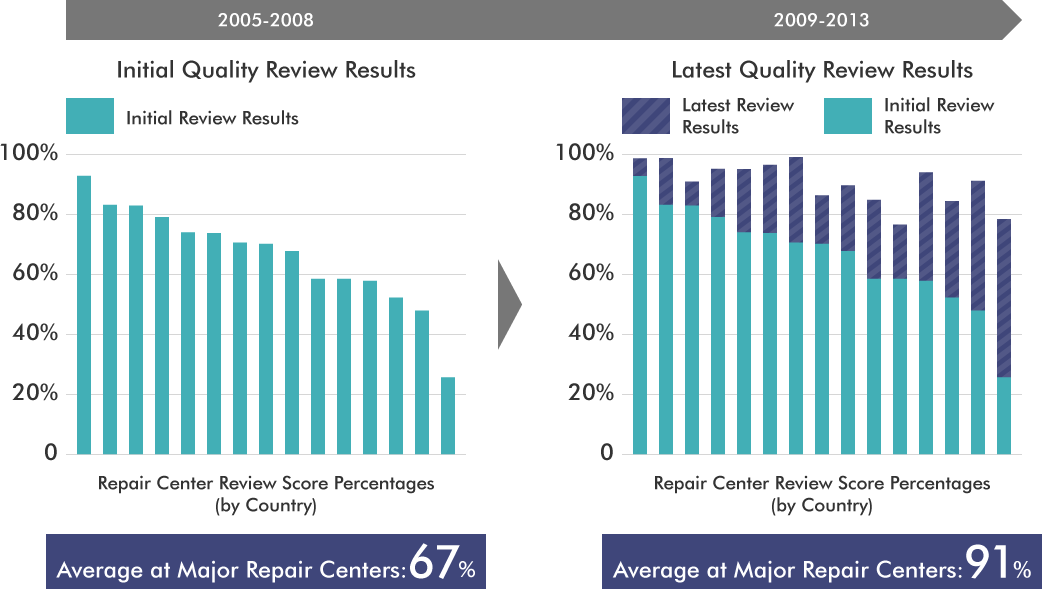
After five years of improvement activities, evaluations at major repair centers were improved by 20% or more.

